The Cambridge IELTS book series 1-19 is an essential resource for those preparing for the IELTS exam. However, note that Cambridge IELTS books difficulty levels can vary significantly. This inconsistency can sometimes pose challenges for learners during their study process. Are later editions more difficult than earlier ones in the Cambridge IELTS series? In the following sections, we will provide a detailed difficulty chart for Cambridge IELTS books 7-19 so that students can effectively organise their study plans.
Difficulty Levels of the Cambridge IELTS Book Series
When assessing the difficulty of IELTS Reading and Listening tests, several key factors include question types, topics, and vocabulary. Candidates can often quickly identify the answers for lower-difficulty question types without spending much time. In contrast, higher-difficulty questions typically include distractors or require more extensive searching, necessitating greater listening and reading comprehension skills and the ability to infer meaning.
IELTS Listening Questions Difficulty Levels
Low Difficulty:
- Form and Table Completion: These questions require candidates to listen for specific information that can be easily extracted from the audio, such as filling in gaps in a table or form.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 10, Test 1. - Sentence Completion: This type involves completing sentences based on the listening material, usually straightforward and focusing on key details.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 11, Test 2. - Short-Answer Questions: These questions typically require concise answers that directly respond to the prompts provided, making them easier to manage for learners.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 12, Test 1.
High Difficulty:
- Multiple Choice: Candidates must discern the correct answer from several options, often including distractors that confuse less prepared learners.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 14, Test 3. - Matching: This question type requires listeners to connect pieces of information, such as matching speakers to their comments, necessitating good retention and comprehension skills.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 13, Test 4. - Plan, Map, Diagram Labeling: Candidates need to accurately label parts of a diagram or map based on the audio, which can be challenging due to the spatial understanding required.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 15, Test 2. - Flow-chart, Summary, Note Completion: These tasks often involve synthesising information from the listening passage and can be demanding due to their complexity and the requirement for detailed comprehension.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 16, Test 4.
IELTS Reading Questions Difficulty Levels
Low Difficulty:
- Identifying Information (True/False/Not Given): Candidates determine whether statements correspond with the text, which often relies on basic comprehension skills.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 7, Test 1. - Multiple Choice: This question type tests understanding through options, allowing for guessing when candidates are unsure.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 8, Test 3. - Sentence Completion: Similar to listening, this requires filling in blanks, making it easier to focus on keywords.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 9, Test 1. - Short-Answer Questions: Candidates provide brief responses, drawing from the text directly, which aids in focusing attention on critical details.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 11, Test 3. - Summary, Note, Table, Flow-chart Completion: These tasks help candidates consolidate information but are generally less complex than high-difficulty tasks.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 12, Test 2.
High Difficulty:
- Diagram Label Completion: This requires a precise understanding of diagrams within the text and can challenge candidates’ spatial comprehension and detailed reading skills.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 10, Test 4. - Identifying a Writer’s Views or Claims (Yes/No/Not Given): This type tests the ability to infer the author’s stance, which can be nuanced and demanding.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 13, Test 2. - Matching Features: Candidates must associate different aspects of the text, requiring comprehensive understanding and analysis.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 14, Test 1. - Matching Headings: This involves identifying the main idea of paragraphs, demanding a strong grasp of the text’s overall structure and themes.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 15, Test 4. - Matching Information: Candidates connect specific details within the text, requiring deep comprehension and recall.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 16, Test 3. - Matching Sentence Endings: This tests understanding the text’s flow and the logical connections between ideas.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 17, Test 1.
Topic Categories in Cambridge IELTS Tests
The topics of the test questions can be divided into three main groups:
- Everyday Topics: Relationships, study and work activities, leisure activities, etc. These topics generally present the lowest difficulty level, making them accessible to all candidates. They are relatable and familiar, providing a comfortable starting point for most test-takers.
- Social Topics: Education, health, technology, etc. These subjects are somewhat more complex, but most candidates typically have foundational knowledge in these areas. Such topics often require candidates to engage critically with societal issues, enhancing their analytical skills.
- Specialised Topics: Engineering, science, artificial intelligence, etc. These themes may pose challenges for some candidates due to their complexity. They require a good command of English and familiarity with specific jargon and concepts that might not be part of general knowledge.
Vocabulary Levels in IELTS Cambridge Tests
The IELTS vocabulary used in the tests can also be categorised into three levels:
- Basic (A1, A2): This vocabulary level includes common, everyday words and phrases that are foundational for beginners in English.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 7. - Intermediate (B1, B2): At this level, vocabulary becomes more varied and context-specific, suitable for those with a moderate grasp of the language.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 8. - Advanced (C1, C2): This level encompasses complex words and expressions often used in academic and professional contexts, suitable for proficient English speakers.
Example: Cambridge IELTS 17.
The difficulty of the vocabulary often aligns with the complexity of the topics. However, in some instances, tests on everyday life or social issues might employ vocabulary related to less common aspects, while specialised topic tests may focus on basic knowledge. This alignment ensures that candidates are challenged appropriately based on their familiarity with the subject matter.
Based on these three factors—question types, topics, and vocabulary—the difficulty levels of Cambridge IELTS Reading and Listening tests from books 7 to 19 are classified into four tiers:
- Medium
- Medium +
- Difficult
- Difficult +
Understanding these classifications can help candidates better prepare for the IELTS exam by focusing their study efforts on areas that align with their skill levels and target scores. Test-takers can approach their preparation with greater confidence and clarity by becoming familiar with the types of questions, the complexity of topics, and the required vocabulary.
Difficulty of Cambridge IELTS Books vs Actual IELTS Exams
The difficulty level of Cambridge IELTS tests compared to real IELTS exams is often perceived as equivalent; however, several important factors must be considered.
- Equivalence in Structure and Difficulty
The Cambridge IELTS book series is meticulously designed to mirror the structure and difficulty of actual IELTS exams. This similarity allows learners to familiarise themselves with the types of questions and requirements of the official test. Most candidates report that practising with these materials significantly enhances their preparedness for the real exam. The consistent structure across listening, reading, writing, and speaking sections helps candidates feel more confident when facing the actual test. - Variation in Difficulty Across Different Tests
Within a single Cambridge IELTS book, different tests may vary in difficulty. Some tests might be more challenging or easier than others, offering a diverse training experience that equips learners to handle varying difficulty levels. Candidates should pay close attention to the specific tests they attempt, evaluating their difficulty to develop a tailored study plan. - Candidate Feedback
- Some candidates believe that certain Cambridge IELTS tests, particularly from volumes 11, 12, and 13, are more difficult than the actual IELTS exams. This perception may stem from differences in topics or vocabulary used in those tests. For instance, academic subjects in these volumes might include many specialised terms unfamiliar to some test-takers, complicating their understanding and response to questions.
- Others find the difficulty level of Cambridge tests quite similar to real IELTS exams. For these candidates, practising with Cambridge materials has proven beneficial in achieving high scores on the official test. These candidates often emphasise that the practice tests have helped them become accustomed to question formats and answering techniques, reducing anxiety during the actual examination.
- Insights on New Test Versions
Newer volumes of Cambridge IELTS, such as IELTS 16 and 17, are often regarded as having higher quality and difficulty levels, featuring updated content more relevant to current trends. These tests better reflect the standards of the contemporary IELTS exam, making it essential for candidates to focus on practising with these newer editions for optimal preparation. - Effective Study Strategies
To achieve the best results, candidates should:- Complete practice tests from the Cambridge IELTS series to become familiar with exam timing and pressures similar to those encountered in the actual test.
- Analyse their performance to identify weaker skills that need improvement.
- Supplement their study with additional resources, including sample tests and online materials, to comprehensively understand question types and formats.
Evaluating the difficulty of Cambridge IELTS tests compared to real IELTS exams is crucial for candidates to create effective study plans. Although there may be differences in difficulty among various tests, practising with Cambridge IELTS materials remains highly beneficial for exam preparation. By mastering test structures, topics, and vocabulary usage, candidates can increase their confidence and readiness for the actual IELTS examination.
How to Use the IELTS Cambridge Difficulty Levels
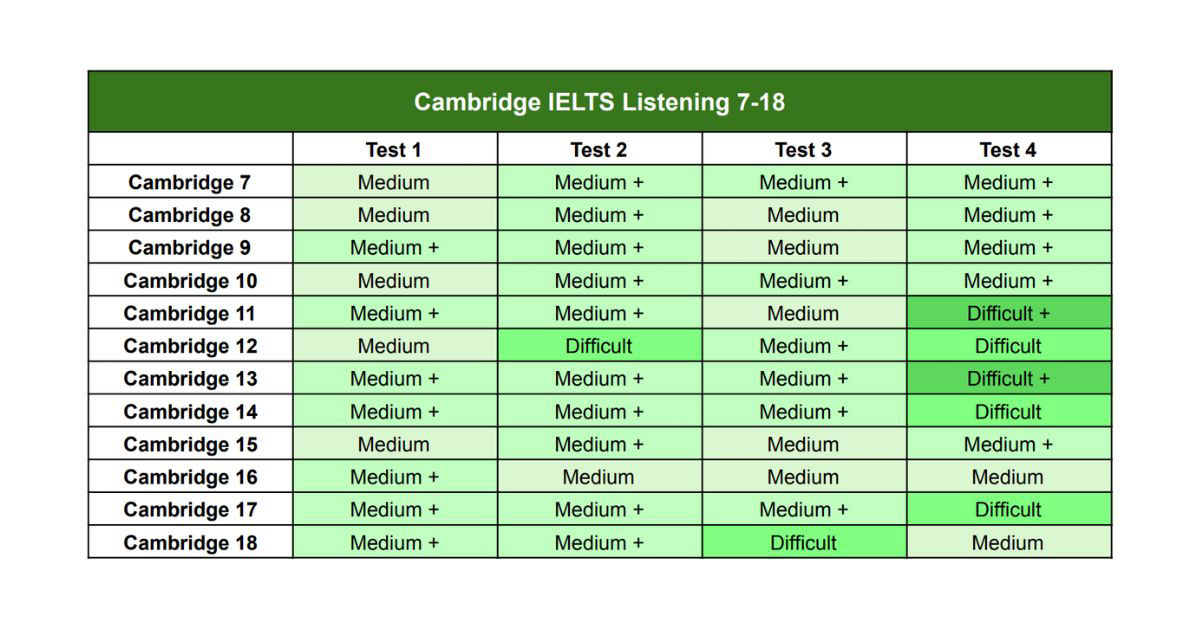
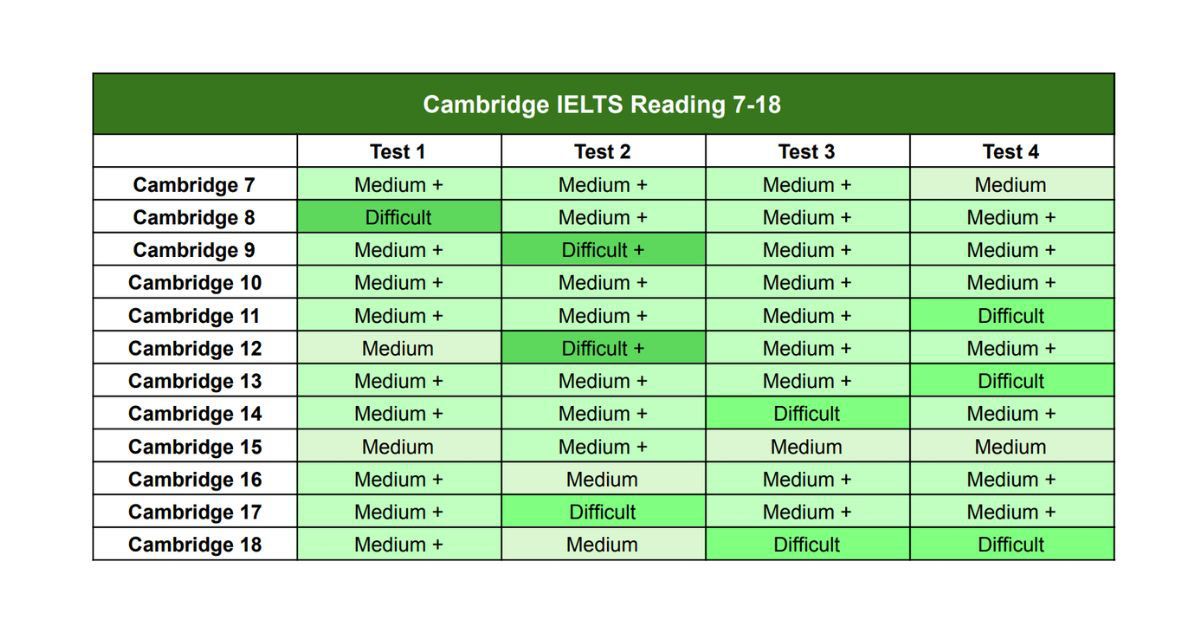
The Cambridge Difficulty Table is an invaluable tool for IELTS preparation using the Cambridge IELTS series. This table analyses the difficulty levels of reading and listening tasks across the Cambridge IELTS books from volume 7 to volume 18 (as of the most recent updates).
To optimise your IELTS preparation, consider the following guidelines on how to effectively utilise the Cambridge Difficulty Table:
Understand the Structure of the Cambridge Difficulty Table: The difficulty table typically includes the following information:
- Test Number: A sequential numbering of the tests within each book.
- Listening Sections: Breakdown of difficulty ratings for each listening section (1, 2, 3, 4).
- Reading Passages: Difficulty assessments for each reading passage (1, 2, 3).
- Overall Difficulty Rating: A general evaluation of the test’s overall difficulty level.
Set Your Target Score: Before starting your preparation, determine your target score. For instance, if you aim to achieve a band score of 7.0, focus on tests that align with this difficulty, such as Cambridge IELTS 7, 10, 16, and 17.
Choose Appropriate Test Materials
a. Select by Band Score:
Use the difficulty table to choose tests that are at or slightly above your current ability level for practice.
- If you are currently at band 5.5 and want to reach band 6.5, begin with tests rated around band 6.0.
- If you are at band 6.5 and aiming for band 7.5, practice with tests rated at or above band 7.0.
b. Select by Test Difficulty Level:
Start with easier tests and gradually increase the difficulty as you build a solid foundation.
- Begin with tests from Cambridge IELTS 7, 8, and 9 (easier levels).
- Progress to Cambridge IELTS 10, 11, and 12 (medium difficulty).
- Advance to Cambridge IELTS 13, 14, 15, and 16 (harder levels).
- Finally, challenge yourself with Cambridge IELTS 17 and 18 (very difficult).
Practice Strategically
- Listening: Focus on the sections where you struggle the most. For example, if sections 3 and 4 are challenging for you, select tests with these sections rated as difficult for targeted practice.
- Reading: Choose more difficult passages to enhance your reading comprehension skills, paying special attention to question types you frequently get wrong.
Assess Your Progress: After each practice test, compare your results with your target score to evaluate your progress. If you notice improvements, gradually select more challenging tests.
Analyse Mistakes: Take time to analyse your errors after each test. Refer to the difficulty table to determine if your mistakes relate to the task’s difficulty level and create a plan to improve in those areas.
The Cambridge Difficulty Table is a valuable resource that helps you select appropriate tests based on your abilities and goals. Utilising it wisely will optimise your preparation process and lead you to achieve your desired results in the IELTS exam.
Cambridge IELTS Books Difficulty FAQs
Is the Cambridge IELTS series harder than the actual test?
The Cambridge IELTS series is not harder than the actual test; it is quite comparable. While some tests may feel easier and others more challenging, the series provides a solid representation of what to expect on test day. The listening sections in the Cambridge books are similar in difficulty to the IELTS exam, so if you score 35 or more in these practice tests, you can likely achieve a band score of 7.5 or higher in the real exam. However, the reading tests can vary in difficulty across different books, with some paragraphs being easier than others. Many test-takers find the reading section of the IELTS exam slightly tougher, typically resulting in a difference of only one or two marks. The writing tasks in the Cambridge series are highly beneficial as they cover a wide range of topics, providing ample practice. While the difficulty of speaking tests can vary depending on the examiner, the Cambridge books help familiarise you with the exam format. While the reading test may be a bit more challenging than the Cambridge books, the series remains an essential resource for all IELTS candidates.
In what order should I practice Cambridge IELTS?
For effective preparation, it’s recommended to practise the Cambridge IELTS series in the following order based on overall difficulty: Start with Cambridge IELTS 15, followed by 7, 16, 10, 8, 11, 12, 13, 14, 17, 18, and finally 9 for Reading. For Listening, begin with 16, then 8, 15, 7, 9, 10, 18, 11, 12, 14, 17, and conclude with 13. While this sequence provides a structured approach, be aware of the variability in difficulty within each book to tailor your practice effectively.
Is it a good idea to finish Cambridge IELTS books 1 to 19?
Yes, completing the Cambridge IELTS series from books 1 to 19 benefits your test preparation. These books offer authentic practice, containing past exam papers, listening CDs, and answer keys, resembling the actual test format and difficulty level. However, it’s advisable to prioritise the more recent books, particularly 15 to 19, to better familiarise yourself with the current test structure and identify areas for improvement. Working through these resources enhances your familiarity with various question types and time constraints and develops your skills across all four language areas—listening, reading, writing, and speaking. Additionally, completing the practice tests allows you to track your progress over time, helping you pinpoint areas that require further focus.
What is the difference between Cambridge IELTS 8, 9, 10, and 11?
The main difference between Cambridge IELTS 8, 9, 10, and 11 lies in their recency and structure. While all books contain authentic past exam papers, newer editions like Cambridge IELTS 11 offer updated content that reflects recent changes in the IELTS test format. Before book 11, there was only one book per year covering both Academic and General Training tests, but from book 11 onwards, these are separated into two distinct volumes, each containing four tests. Additionally, starting from Cambridge IELTS 12, there have been modifications to the reading module where questions may not follow the text order. For the best preparation, it is advisable to prioritise recent editions while benefiting from the insights from older books.
Are Cambridge IELTS Series 1-19 enough for actual IELTS tests?
Yes, the Cambridge IELTS books are highly regarded as effective preparation tools for the actual IELTS exam. With 19 volumes available, particularly those numbered 12 and above, they closely replicate the difficulty level of the real test. The latest release, Cambridge IELTS Academic Book 19, offers the most accurate representation of the exam format and content. Many test-takers have successfully used these resources to improve their scores, often reporting increased confidence and time management during their exams. While there may be some variation in difficulty among the Cambridge tests, they remain a solid foundation for identifying and addressing weaknesses before taking the official IELTS test.
Is Cambridge IELTS 19 Academic harder than Cambridge IELTS 16?
Cambridge IELTS Book 19 is not necessarily harder than Book 16; the difficulty can vary based on individual perception and performance. Each book in the Cambridge IELTS series includes authentic past exam papers, but the specific difficulty level of tests can differ. Generally, newer books, including Cambridge IELTS 19 Academic, may incorporate more recent test formats and question types, which can feel more challenging for some test-takers. However, it’s essential to practice with both books to identify your strengths and weaknesses, as this will provide a comprehensive preparation experience.
