You should spend about 20 minutes on this task.
The two pie charts below show some employment patterns in Great Britain in 1992. Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
You should write at least 150 words.
Sample Answer 1
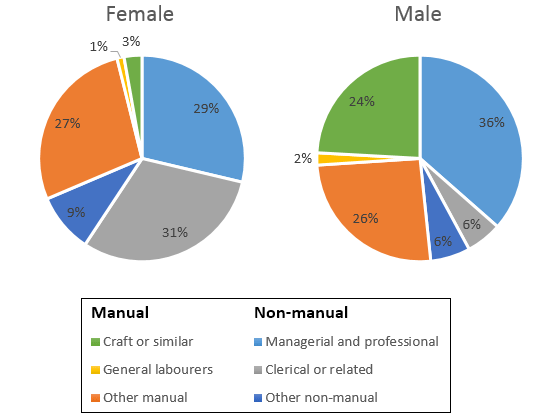
The pie charts outline the employment scenario of British males and females in six job sectors in 1992. Males predominantly did manual jobs, whereas a higher percentage of females did clerical jobs. Moreover, managerial and craft-related positions were engaged by a higher proportion of both genders.
As the illustration indicates, more percentages of British males worked in manual sectors, except in craft-related industries, compared to their female counterparts. For instance, 2% of general laborers in Great Britain were men, while the female laborers’ ratio was half of that. Moreover, 24% of males worked in numerous other manual jobs, while this was only 3% for females. Nevertheless, 27% of females in craft-related industries marginally exceeded the ratio of males in the same sector.
Looking further into the data, non-manual professions included managerial & professional, clerical, and other non-manual jobs. Interestingly, employment rates of females in clerical were five times higher than that of males. This is the job category that many females (31%) we engaged in. Besides, over one-third of males were in managerial and professional jobs, while almost 30% of females were in these positions.
Sample Answer 2
The charts provide information on the proportion of males and females in employment in 6 broad categories, divided into manual and non-manual occupations. In general, more women work in non-manual fields than in manual occupations, and the reverse is true for men.
In non-manual occupations, while a more significant percentage of working women than men are found in clerical-type positions, a smaller percentage of women than men are employed in managerial and professional situations. The percentage of women employed in other non-manual occupations is slightly larger than the percentage of men in these occupations.
In manual employment, the most significant difference between the two sexes is in the employment of craft workers, where males make up 24% of the workforce and females just 3%. Furthermore, the percentage of women working as general laborers is tiny, only 1%. There is not a great deal of difference between the percentage of men doing other forms of manual work (26%) and women in other manual work (27%).
In summary, the two charts clearly show that women do not have the same access as men to certain types of employment.
