» You should spend about 20 minutes on this task.
The chart below shows the different levels of post-school qualifications in Australia and the proportion of men and women who held them in 1999.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant.
» Write at least 150 words.
Sample Answer 1
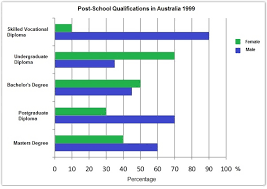
The bar graph compares post-school qualification in Australia based on gender for the year 1999. Generally speaking, more male achieved their post-school degrees in skilled vocational diploma, Masters degree and postgraduate diploma than females did while for more female, the highest educational qualification was undergraduate diploma and Bachelor’s degree.
According to the data, Australian male and female who achieved their post-school degrees in 1999 were classified into five categories. ‘Female post-school qualified’ surpassed their male counterpart in undergraduate diploma and bachelor’s degree as they a smaller ratio of females attended post-graduation courses. For the undergraduate diploma, the percentage of females was 70% compared to the only 35% male. Male were predominating in percentage when it comes to master’s degree, postgraduate diploma and skilled vocational diploma. 90% male completed skilled vocational diploma and the remaining 10% was female. It is worth noticing that, though many females completed their bachelor degree, the percentage decreased in masters degree level whereas 60% male completed it.
Sample Answer 2
The bar chart compares post-school educational attainment among men and women in Australia in 1999.
As a whole, men were ahead of women in terms of their highest educational qualifications in Australia, and three out of five types of post-school educational qualifications, namely – post-graduate diploma, skilled vocational diploma and masters degree, were mostly attended by men.
In details, those who had a post-graduate diploma and Master’s degree were dominated by 70% and 60% men respectively. The ratio of women who had post-graduation qualification was much lower. Another important aspect of the graph is that there was a remarkable number of men, 90%, who took up a ‘skilled vocational diploma course’ which left women to only just a tenth. Since men continued their education and achieved post-graduate qualifications, females with an undergraduate diploma much outweighed the ratio of males. Finally, the proportion of male whose highest education was a bachelor’s degree was about 45%, whereas the females’ ratio was somewhat more than that.
[ Written by – Kenny Boy ]
Sample Answer 3
The illustration compares the post-school qualifications of Australian male and female in 1999. As is observed, more female’s highest educational qualification was undergraduate diploma and bachelor degree while male outnumbered female in higher qualification levels and skilled education.
According to the chart, almost 90% of males had a skilled vocational diploma, while only approximately 10% of females had the same qualifications. Nearly 70% of women’s highest qualification was an undergraduate diploma, and this ratio is more than twice than that of males. In terms of males and females whose highest education was a bachelor degree, females were slightly ahead of male with a ratio of 50%. But if we consider the females and males who had obtained post-graduation degrees, males were well ahead of females. 70% of post-graduate diplomas were completed by males and 60% master’s degree was completed by females. On the contrary, only 30% of women finished a post-graduate diploma and four out of ten master’s degree holders were females.
[Written by – Veta]
