READING PASSAGE 1
Working in the movies
When people ask French translator Virginie Verdier what she does for a living, it must be tempting to say enigmatically: ‘Oh me? I’m in the movies’. It’s strictly true, but her starring role is behind the scenes. As translating goes, it doesn’t get more entertaining or glamorous than subtitling films. If you’re very lucky, you get to work on the new blockbuster films before they’re in the cinema, and if you’re just plain lucky, you get to work on the blockbuster movies that are going to video or DVD.
The process starts when you get the original script and a tape. ‘We would start with translating and adapting the film script. The next step is what we call ‘timing’, which means synchronising the subtitles to the dialogue and pictures.’ This task requires discipline. You play the film, listen to the voice and the subtitles are up on your screen ready to be timed. You insert your subtitle when you hear the corresponding dialogue and delete .it when the dialogue finishes. The video tape carries a time code which runs in hours, minutes, seconds and frames. Think of it as a clock. The subtitling unit has an insert key to capture the time code where you want the subtitle to appear. When you press the delete key, it captures the time code where you want the subtitle to disappear. So each subtitle would Subtitling is an exacting part of the translation profession. Melanie Leyshon talks to Virginie Verdier of London translation company VSI about the glamour and the grind. Virginie is quick to point out that this is as exacting as any translating job. You work hard. It’s not all entertainment as you are doing the translating. You need all the skills of a good translator and those of a top-notch editor. You have to be precise and, of course, much more concise than in traditional translation work.
‘have an ‘in’ point and an ‘out’ point which represent the exact time when the subtitle comes in and goes out. This process is then followed by a manual review, subtitle by subtitle, and time- codes are adjusted to improve synchronisation and respect shot changes. This process involves playing the film literally frame by frame as it is essential the subtitles respect the visual rhythm of the film.’
Different subtitlers use different techniques. ‘I would go through the film and do the whole translation and then go right back from the beginning and start the timing process. But you could do it in different stages, translate let’s say 20 minutes of the film, then time this section and translate the next 20 minutes, and so on. It’s just a different method.’
For multi-lingual projects, the timing is done first to create what is called a ‘spotting list’, a subtitle template, which is in effect a list of English subtitles pre-timed and edited for translation purposes. This is then translated and the timing is adapted to the target language with the help of the translator for quality control.
‘Like any translation work, you can’t hurry subtitling,’ says Virginie. ‘If subtitles are translated and timed in a rush, the quality will be affected and it will show.’ Mistakes usually occur when the translator does not master the source language and misunderstands the original dialogue. ‘Our work also involves checking and reworking subtitles when the translation is not up to standard. However, the reason for redoing subtitles is not just because of poor quality translation. We may need to adapt subtitles to a new version of the film: the time code may be different. The film may have been edited or the subtitles may have been created for the cinema rather than video. If subtitles were done for cinema on 35mm, we would need to reformat the timing for video, as subtitles could be out of synch or too fast. If the translation is good, we would obviously respect the work of the original translator.’
On a more practical level, there are general subtitling rules to follow, says Virginie. ‘Subtitles should appear at the bottom of the screen and usually in the centre.’ She says that different countries use different standards and rules. In Scandinavian countries and Holland, for example, subtitles are traditionally left justified. Characters usually appear in white with a thin black border for easy reading against a white or light background. We can also use different colours for each speaker when subtitling for the hearing impaired. Subtitles should have a maximum of two lines and the maximum number of characters on each line should be between 32 and 39. Our company standard is 37 (different companies and countries have different standards).’
Translators often have a favourite genre, whether it’s war films, musicals, comedies (one of the most difficult because of the subtleties and nuances of comedy in different countries), drama or corporate programmes. Each requires a certain tone and style. ‘VSI employs American subtitlers, which is incredibly useful as many of the films we subtitle are American,’ says Virginie. ‘For an English person, it would not be so easy to understand the meaning behind typically American expressions, and vice-versa.’
Questions 1-5
Complete the flow chart below. Use NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS from the passage for each answer.
THE SUBTITLING PROCESS
Stage 1: Translate and adapt the script
Stage 2: (1)…………………….-matching the subtitles to what said Involves recording time codes by using the (2)……………….keys.
Stage 3: (3)……………………….– in order to make the (4)……………………..better
Multi – lingual project
Stage 4: Produce something known as a (5)……………………..and translate that
Questions 6-9
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 1? In boxes 6-9 on your answer sheet write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN If there is no information on this
6. For translators, all subtitling work on films is desirable.
7. Subtitling work involves a requirement that does not apply to other translation work.
8. Some subtitling techniques work better than others.
9. Few people are completely successful at subtitling comedies.
Questions 10-13
Complete the sentences below with words from Reading Passage I. Use NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS for each answer.
Poor subtitling can be a result of the subtitler not being excellent at (10)……………………
To create subtitles for a video version of a film, it may be necessary to (11)…………………….
Subtitles usually have a (12)……………………….around them.
Speakers can be distinguished from each other for the benefit of (13)…………………..
READING PASSAGE 2
Complementary and alternative medicine
Is complementary medicine hocus-pocus or does it warrant large-scale scientific investigation? should science range beyond conventional medicine and conduct research on alternative medicine and the supposed growing links between mind and body? This will be hotly debated at the British Association for the Advancement of Science.
One Briton in five uses complementary medicine, and according to the most recent Mintel survey, one in ten uses herbalism or homoeopathy. Around £130 million is spent on oils, potions and pills every year in Britain, and the complementary and alternative medicine industry is estimated to be worth £1.6 billion. With the help of Professor Edzard Ernst, Laing chair of complementary medicine at The Peninsula Medical School, Universities of Exeter and Plymouth, we asked scientists their views on complementary and alternative medicine. Seventy-five scientists, in fields ranging from molecular biology to neuroscience, replied.
Surprisingly, our sample of scientists was twice as likely as the public to use some form of complementary medicine, at around four in 10 compared with two in 10 of the general population. Three quarters of scientific users believed they were effective. Acupuncture, chiropractic and osteopathy were the most commonly used complementary treatments among scientists and more than 55 per cent believed these were more effective than a placebo and should be available to all on the National Health Service.
Scientists appear to place more trust in the more established areas of complementary and alternative medicine, such as acupuncture, chiropractic and osteopathy, for which there are professional bodies and recognised training, than therapies such as aromatherapy and spiritual healing. ‘Osteopathy is now a registered profession requiring a certified four-year degree before you can advertise and practise,’ said one neuroscientist who used the therapy. Nearly two thirds of the scientists who replied to our survey believed that aromatherapy and homoeopathy were no better than placebos, with almost a half thinking the same of herbalism and spiritual thinking. Some of the comments we received were scathing, even though one in ten of our respondents had used homeopathy. ‘Aromatherapy and homoeopathy are scientifically nonsensical,’ said one molecular biologist from the University of Bristol. Dr Romke Bron, a molecular biologist at the Medical Research Council Centre at King’s College London, added: ‘Homoeopathy is a big scam and I am convinced that if someone sneaked into a homoeopathic pharmacy and swapped labels, nobody would notice anything.’
Two centuries after homeopathy was introduced, it still lacks a watertight demonstration that it works. Scientists are happy that the resulting solutions and sugar baffled by how they can do anything.
Both complementary and conventional medicine should be used in routine health care, according to followers of the ‘integrated health approach’, who want to treat an individual ‘as a whole’. But the scientists who responded to our survey s expressed serious concerns about this approach, with more than half believing that integrated medicine was an attempt to bypass rigorous scientific testing. Dr Bron said: ‘There is an awful lot of bad science going on in alternative medicine and the general public has a hard time to distinguish between scientific myth and fact. It is absolutely paramount to maintain rigorous quality control in health care. Although the majority of alternative health workers mean well, there are just too many frauds out there preying on vulnerable people.’
One molecular biologist from the University of Warwick admitted that ‘by doing this poll I have realised how shamefully little I understand about alternative therapy. Not enough scientific research has been performed. There is enough anecdotal evidence to suggest that at least some of the alternative therapies are effective for some people, suggesting this is an area ripe for research.’
When asked if complementary and alternative medicine should get more research funding, scientists believed the top three (acupuncture, chiropractic and osteopathy) should get money, as should herbalism. It seems that therapies based on physical manipulation or a known action – like the active ingredients in a herb on a receptor in the body – are the ones that the scientific community has faith in. Less than a quarter thought that therapies such as aromatherapy, homoeopathy and spiritual healing should get any funding.
Scientists believed that the ‘feelgood’ counselling effect of complementary medicine and the time taken to listen to patients’ problems was what worked, rather than any medicinal effect. In contrast, the average visit to the doctor lasts only eight minutes, says the British Medical Association. Dr Stephen Nurrish, a molecular biologist at University College London, said: ‘Much of the benefit people get from complementary medicine is the time to talk to someone and be listened to sympathetically, something that is now lacking from medicine in general.’
But an anonymous neuroscientist at King’s College London had a more withering view of this benefit: ‘On the validity of complementary and alternative medicines, no one would dispute that ‘feeling good’ is good for your health, but why discriminate between museum-trip therapy, patting-a-dog therapy and aromatherapy? Is it because only the latter has a cadre of professional ‘practitioners’?’
There are other hardline scientists who argue that there should be no such thing as complementary and alternative medicine. As Professor David Moore, director of the Medical Research Council’s Institute for Hearing Research, said: ‘Either a treatment works or it doesn’t. The only way to determine if it works is to test it against appropriate controls (that is, scientifically).’
Questions 14-19
Look at the following views (Questions 14—19) and the list of people below them. Match each view with the person expressing it in the passage. NB You may use any letter more than once.
14. Complementary medicine provides something that conventional medicine no longer does.
15. It is hard for people to know whether they are being told the truth or nor.
16. Certain kinds of complementary and alternative medicine are taken seriously because of the number of people making money from them.
17. Nothing can be considered a form of medicine unless it has been proved effective.
18. It seems likely that some forms of alternative medicine do work.
19. One particular kind of alternative medicine is a deliberate attempt to cheat the public.
List of People
A Dr Romke Bron
B a molecular biologist from the University of Warwick
C Dr Stephen Nurrish
D a neuroscientist at King’s College London
E Professor David Moore
Questions 20-22
Complete each sentence with the correct ending A-F from the box below.
20. The British Association for the Advancement of Science will be discussing the issue of
21. A recent survey conducted by a certain organisation addressed the issue of
22. The survey in which the writer of the article was involved gave information on
A what makes people use complementary rather than conventional medicine.’
B how many scientists themselves use complementary and alternative medicine.
C whether alternative medicine should be investigated scientifically.
D research into the use of complementary and conventional medicine together.
E how many people use various kinds of complementary medicine.
F the extent to which attitudes to alternative medicine are changing
Questions 23-26
Classify the following information as being given about
A acupuncture
B aromatherapy
C herbalism
D homoeopathy
23. scientists believe that it is ineffective but harmless.
24. Scientists felt that it could he added to the group of therapies that deserved to be provided with resources for further investigation.
25. Scientists felt that it deserved to be taken seriously because of the organised way in which it has developed.
26. A number of scientists had used it, but harsh criticism was expressed about it
READING PASSAGE 3
The cloud messenger
A Luke Howard had been speaking for nearly an hour, during which time his audience had found itself in a state of gradually mounting excitement. By the time that he reached the concluding words of his address, the Plough Court laboratory was in an uproar. Everyone in the audience had recognized the importance of what they had just heard, and all were in a mood to have it confirmed aloud by their friends and neighbours in the room. Over the course of the past hour, they had been introduced not only to new explanations of the formation and lifespan of clouds, but also to a poetic new terminology: ‘Cirrus’, ‘Stratus’, ‘Cumulus’, ‘Nimbus’, and the other names, too, the names of intermediate compounds and modified forms, whose differences were based on altitude, air temperature and the shaping powers of upward radiation. There was much that needed to be taken on board.
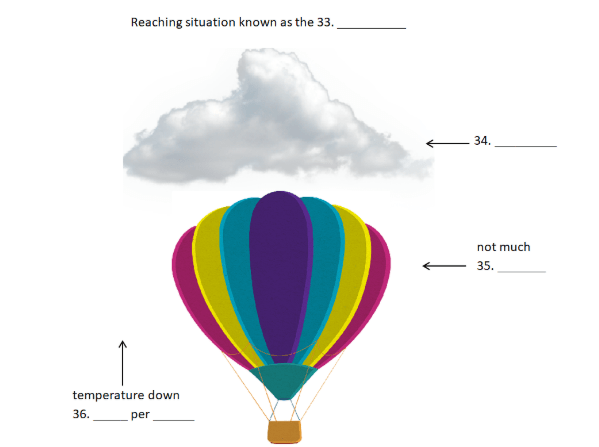
B Clouds, as everyone in the room would already have known, were staging posts m the rise and fall of water as it made its way on endless compensating journeys between the earth and the fruitful sky. Yet the nature of the means of their exact construction remained a mystery to most observers who, on the whole, were still in thrall to the vesicular or ‘bubble’ theory that had dominated meteorological thinking for the better part of a century. The earlier speculations, in all their strangeness, had mostly been forgotten or were treated as historical curiosities to be glanced at, derided and then abandoned. Howard, however, was adamant that clouds were formed from actual solid drops of water and ice, condensed from their vaporous forms by the fall in temperature which they encountered as they ascended through the rapidly cooling lower atmosphere. Balloon pioneers during the 1780s had continued just how cold it could get up in the realm of the clouds: the temperature fell some 6.5″C for every thousand metres they ascended. By the rime the middle of a major cumulus cloud had been reached, the temperature would have dropped to below freezing, while the oxygen concentration of the air would be starting to thin quire dangerously. That was what the balloonists meant by ‘dizzy heights’.
C Howard was not, of course, the first to insist that clouds were best understood as entities with physical properties of their own, obeying the same essential laws which governed the rest of the natural world (with one or two interesting anomalies: water, after all, is a very strange material). It had long been accepted by many of the more scientifically minded that clouds, despite their distance and their seeming intangibility, should be studied and apprehended like any other objects in creation.
D There was more, however, and better. Luke Howard also claimed that there was a fixed and constant number of basic cloud types, and this number was not (as the audience might have anticipated) in the hundreds or the thousands, like the teeming clouds themselves, with each as individual as a thumbprint. Had this been the case, it would render them both unclassifiable and unaccountable; just so many stains upon the sky. Howard’s claim, on the contrary, was that there were just three basic families of cloud, into which every one of the thousands of ambiguous forms could be categorized with certainty. The clouds obeyed a system and, once recognized in outline, their basic forms would be ‘as distinguishable from each other as a tree from a hill, or the latter from a lake’, for each displayed the simplest possible visual characteristics.
E The names which Howard devised tor them were designed to convey a descriptive sense of each cloud type’s outward characteristics (a practice derived from the usual procedures of natural history classification), and were taken from the Latin, for ease of adoption by the learned of different nations’: Cirrus (from the Latin for fibre or hair), Cumulus (from the Latin for heap or pile) and Stratus (from the Latin for layer or sheet). Clouds were thus divided into tendrils, heaps and layers: the three formations at the heart of their design. Howard then went on to name four other cloud types, all of which were either modifications or aggregates of the three major families of formation. Clouds continually unite, pass into one another and disperse, but always in recognizable stages. The rain cloud Nimbus, for example (from the Latin for cloud), was, according to Howard, a rainy combination of all three types, although Nimbus was reclassified as nimbostratus by meteorologists in 1932, by which time the science of rain had developed beyond all recognition.
F The modification of clouds was a major new idea, and what struck the audience most vividly about it was its elegant and powerful fittingness. All of what they had just heard seemed so clear and so self-evident. Some must have wondered how it was that no one – not even in antiquity – had named or graded the clouds before, or if they had, why their efforts had left no trace in the language. How could it he that the task had been waiting for Howard, who had succeeded in wringing a kind of exactitude from out of the vaporous clouds? Their forms, though shapeless and unresolved, had at last, it seemed, been securely grasped. Howard had given a set of names to a radical fluidity and impermanence that seemed every bit as magical, to that first audience, as the Eskimo’s fabled vocabulary of snow.
Questions 27-32
Reading Passage 3 has six paragraphs A-F. Choose the correct heading for each paragraph from the list of headings below.
List of Headings
i An easily understood system
ii Doubts dismissed
iii Not a totally unconventional view
iv Theories compared
v A momentous occasion
vi A controversial use of terminology
vii Initial confusion
viii Previous beliefs replaced
ix More straightforward than expected
x An obvious thing to do
27. Paragraph A
28. Paragraph B
29. Paragraph C
30. Paragraph D
31. Paragraph E
32. Paragraph F
Questions 33-36
Label the diagram below. Choose NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER from the passage for each answer.
Questions 37-40
Reading Passage 3 has six paragraphs labelled A-F. Which paragraph contains the following information? NB You may use any letter more than once.
37. an example of a modification made to work done by Howard
38. a comparison between Howard’s work and another classification system.
39. a reference to the fact that Howard presented a very large amount of information
40. an assumption that the audience asked themselves a question
ANSWER