You should spend about 20 minutes on this task.
The table below shows the percentage use of four different fuel types to generate electricity in five Asian countries in 2005. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
Write at least 150 words.
Sample Answer
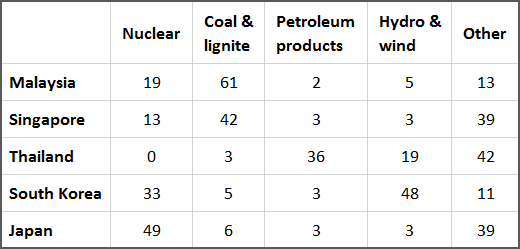
The table shows different sources of fuel for producing electricity and their percentage use in five Asian countries in 2005. Generally, the five countries showed a significant difference in their patterns of consumption. Taking nuclear fuel first, Japan had the highest percentage at 49%, with South Korea second at 33%. In marked contrast, Thailand used no nuclear power at all. Turning to Coal and Lignite, Malaysia and Singapore used this to generate a large proportion of their electricity (61% and 42% respectively), a much higher percentage than the remaining countries.
Regarding Petroleum products, Thailand produced 36% of its electricity from this source. In comparison, the other countries only generated 3% or less of their electricity from this fuel. However, Hydro and Wind reveal another pattern with South Korea producing almost half of its electricity (48%) this way (over twice as high as Thailand which had the second highest percentage at 19%). Finally, a significant amount was produced from other sources with three countries (Singapore, Thailand and Japan) generating around 40% of their electricity from other fuels. Overall, it can be seen that there was a significant variation in which fuels countries used to generate their electricity.
(196 words)
